VR Medical Training
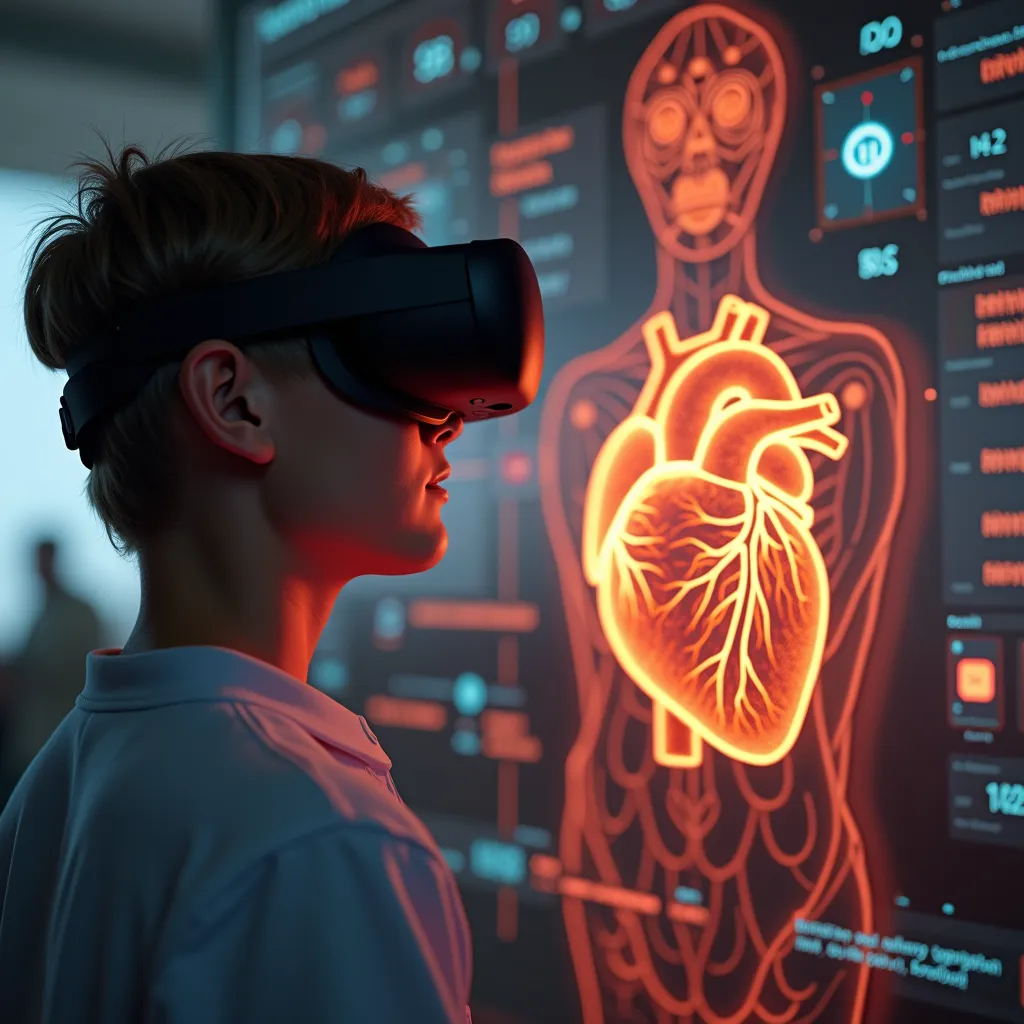
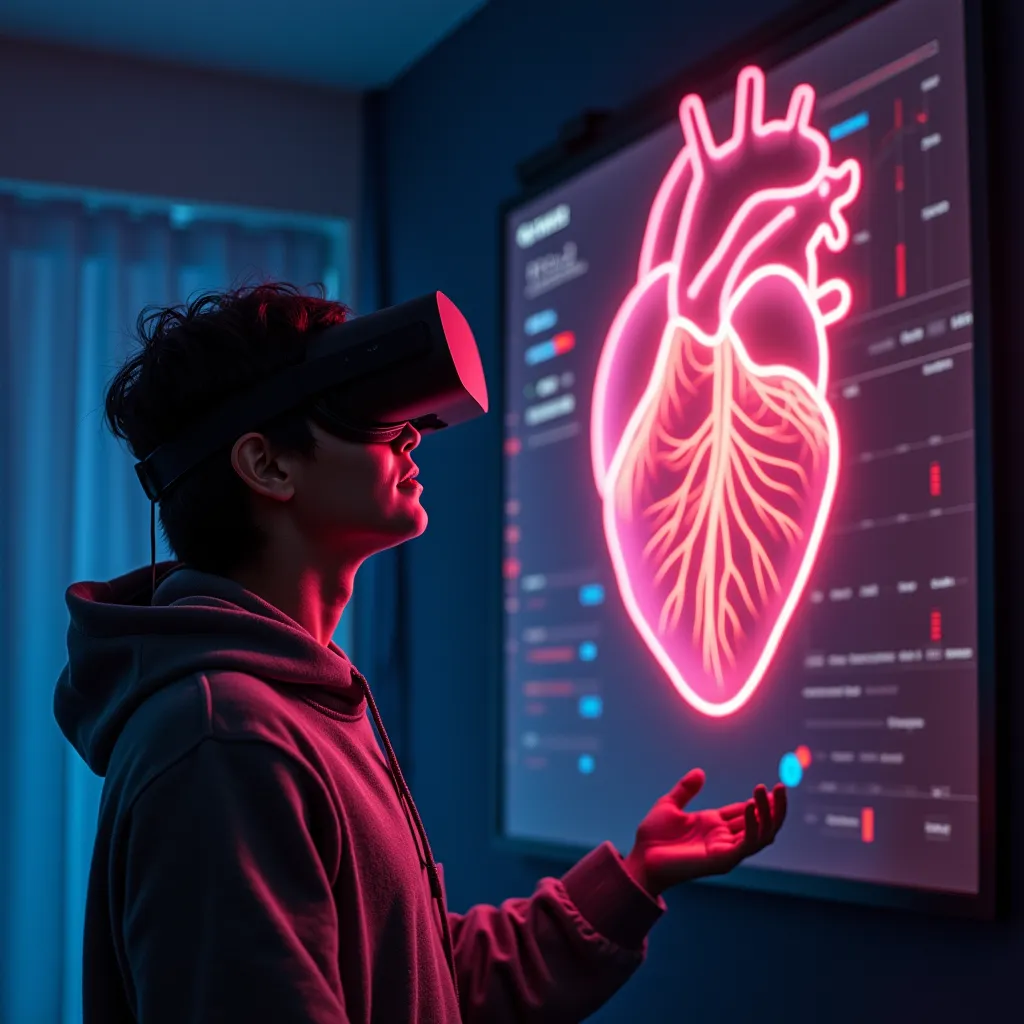
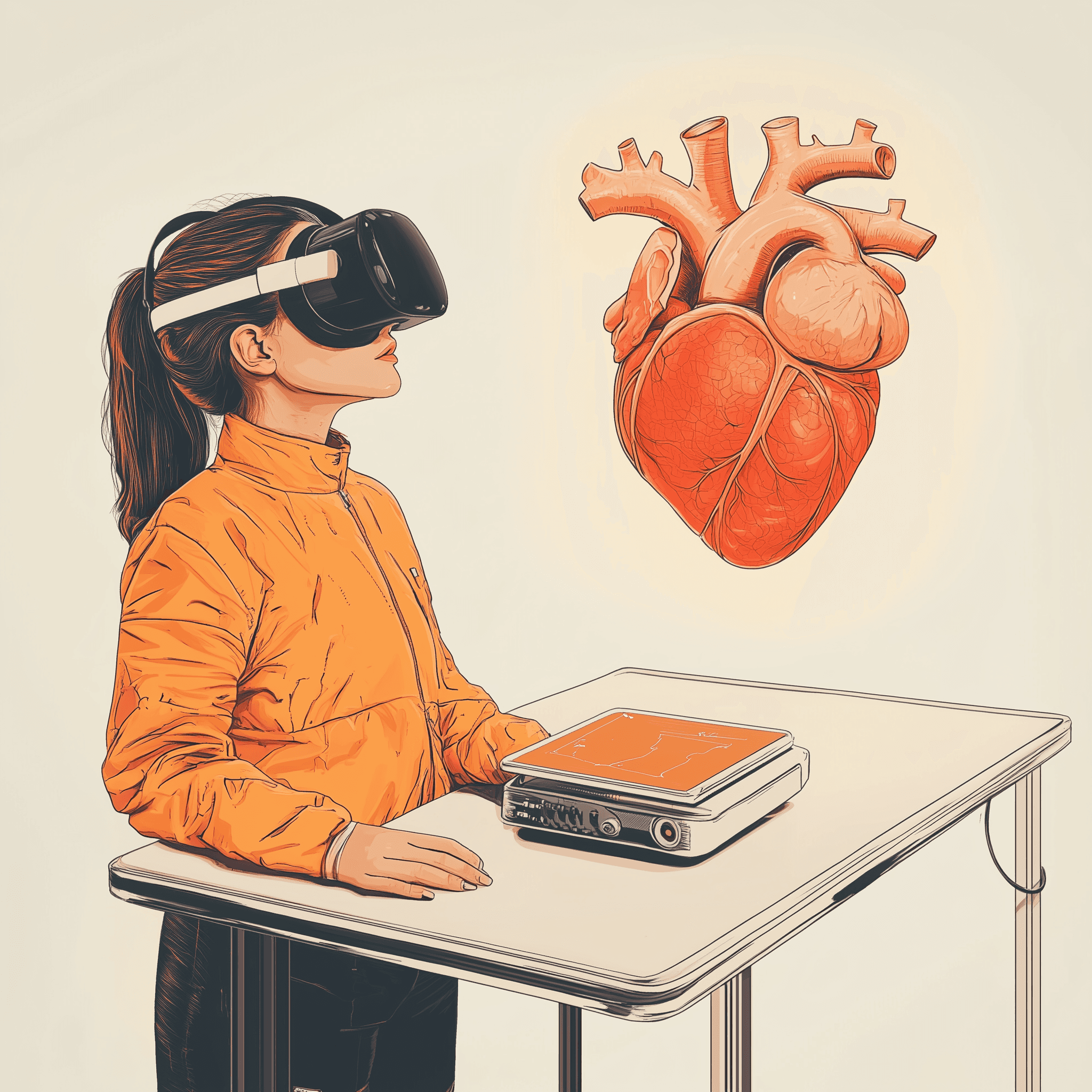
Interactive 3D VR model for immersive medical training, simplifying anatomy for professionals.
VR
Published on: 23. Oktober 2024
The Impulse
A leading medical company sought an innovative solution to improve the training and learning experience for medical professionals. They wanted an interactive tool that could visually explain complex human anatomy, making it easier for learners to understand the functions and structures of key organs like the liver, heart, and circulatory system.
The Challenge
Complex Anatomy Visualization: The system needed to display intricate details of human organs, including veins, arteries, nerves, and their functions, in a way that was easily comprehensible to medical professionals at all levels.
Interactivity and Precision: The challenge was to create a virtual reality (VR) solution that not only showcased 3D medical diagrams but also allowed users to interact with and explore these diagrams from all angles.
Comprehensive Training Tool: The VR model needed to go beyond visuals and be a comprehensive training tool, integrating medical knowledge for deeper insights and understanding.
Solution Approach
We developed a VR-powered solution that transformed medical training by creating detailed, interactive 3D diagrams of vital organs. Here's how we addressed the challenges:
Immersive 3D Diagrams: We designed detailed 3D models of the liver, heart, and other organs, layering them to show veins, arteries, nerves, and internal structures in high detail.
Interactive VR Model: The VR solution allowed medical professionals to view organs from all angles, zoom in on specific areas, and peel back layers to understand the anatomy and functions more thoroughly.
Integrated Medical Knowledge: The model included medical insights and data, helping users to not only view the organs but also learn the medical principles behind each structure and system.
The Results
a. Cost, Time, and Efficiency:
The VR solution significantly reduced the need for physical models and cadavers, leading to cost savings for medical institutions. Training time was optimized as students could access the VR model repeatedly, enhancing learning efficiency
Enhanced Learning Efficiency: A study by PwC found that VR-trained learners were up to 4 times more focused during training than their e-learning peers and 1.5 times more focused than those in traditional classrooms.
Cost-Effective Training: Research by Deloitte highlights that VR training is more cost effective compared to traditional methods, making it a long-term cost-effective solution.
Reduced Training Time: VR learners completed training faster than traditional classroom learners. Additionally, organizations utilizing VR simulations can reduce training time significantly,, according to Deloitte.
b. Design Features:
Layered 3D Organ Models: Each organ was broken down into layers, allowing learners to explore individual parts in great detail.
Full 360-Degree Interactivity: Users could rotate and zoom into each organ to view them from any angle, providing a comprehensive understanding.
Medically Accurate Data: The VR model integrated real-time medical knowledge, offering users accurate insights into organ functions and structures.
Further Use Cases
Medical Schools: Use in medical schools to provide students with an immersive, interactive learning tool.
Surgical Training: Application in specialized training for surgeons to understand the complexity of human anatomy before performing procedures.
Patient Education: Help patients understand their medical conditions through an immersive visualization of their organs.
Updated on: 30. Oktober 2024